Who gets the money from EU ETS?
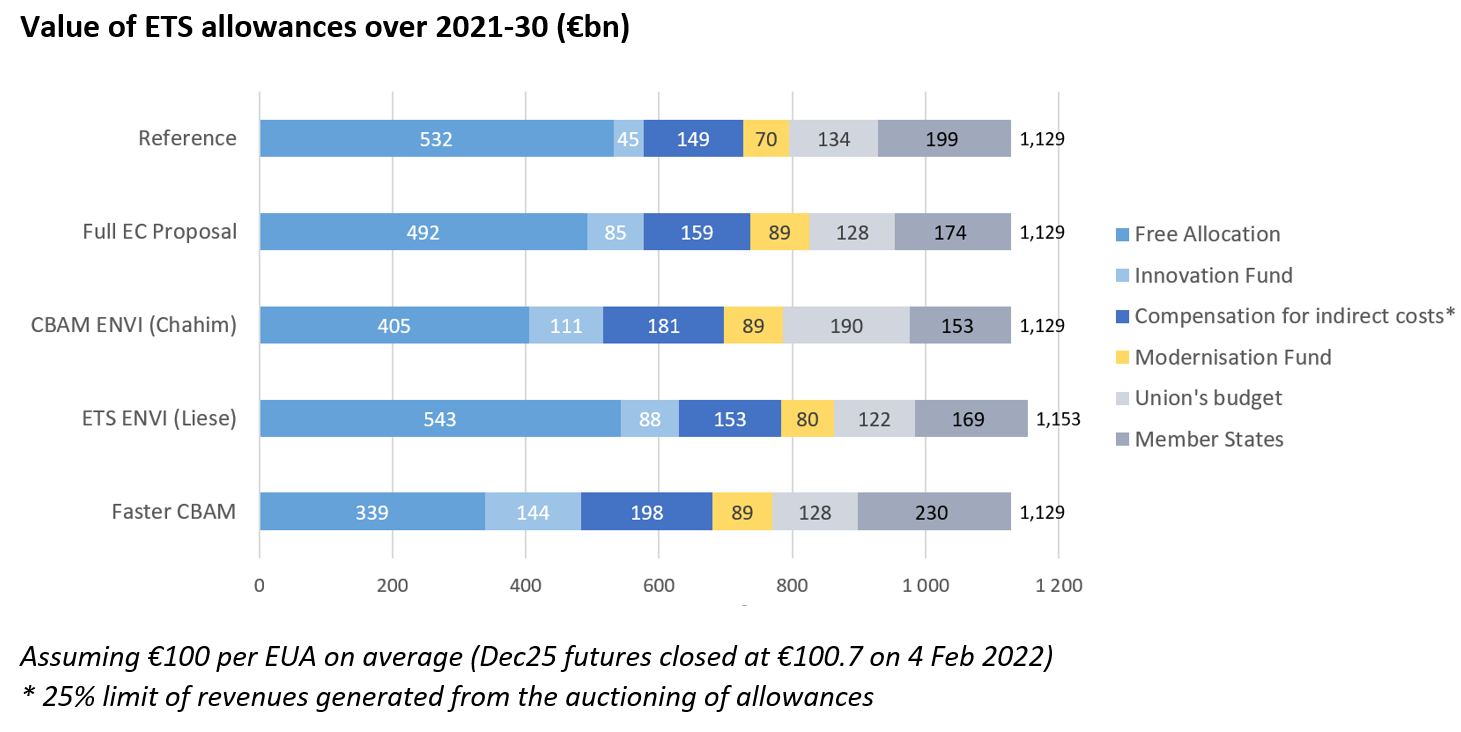
Where do EU ETS revenues go
Revenues from the sale of allowances in the EU ETS mostly feed into Member States' budgets. Allowances are also auctioned to supply the funds supporting innovation in low-carbon technologies and the energy transition: the Innovation FundEN. and the Modernisation FundEN. .
How does the EU emissions trading scheme work
The EU ETS follows a 'cap-and-trade' approach: the EU sets a cap on how much CO2 can be emitted – which decreases each year – and companies need to have a European Emission Allowance (EUA) for every tonne of CO2 they emit within one calendar year. They receive or buy these permits – and they can trade them.
How are EU ETS allowances allocated
Auctioning is the default method for allocating emission allowances to companies participating in the EU emissions trading system (EU ETS).
Who participates in EU ETS
All combustion plants with a thermal capacity of at least 20 MW are obliged to participate in the EU ETS. Plants in energy-intensive industries such as steelworks, cement works and refineries must exceed a sector-specific production output in order to be subject to the emissions trading obligation.
Why did EU ETS fail
Strong industrial lobbying led to its failure. In 2005, EU succeeded to negotiate and introduce an alternative to a carbon tax known under the European Union Emissions Trading Systems or EU ETS.
Which countries receive the most EU funding
Poland was the biggest net recipient of the EU budget (getting more back than it contributed in the first place), followed by Greece, Romania, Hungary and Portugal.
Has the EU ETS been successful
Greenhouse gas emissions from stationary installations in the EU ETS decreased from 1,530 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) in 2019 to 1,355MtCO2e in 2020, a reduction of 11.4%. This represents the largest drop in emissions since the ETS began operating in 2005.
How is EU funding distributed
Approximately 94% of the EU budget funds programmes and projects both within member states and outside the EU. Less than 7% of the budget is used for administrative costs, and less than 3% is spent on EU civil servants' salaries.
How much foreign aid does the EU give
In 2021, according to the European Commission , the EUI provided EUR28. 7 billion ( US$ 30.2 billion) in support to partner countries for COVID-19 response (not all of this is counted as ODA ).
How do you get paid for carbon credits
There are several options for selling carbon credits, including compliance carbon markets, voluntary carbon markets, and carbon exchanges. Compliance carbon markets are regulated by governments and operate under a cap-and-trade system.
Is the EU ETS successful
Greenhouse gas emissions from stationary installations in the EU ETS decreased from 1,530 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) in 2019 to 1,355MtCO2e in 2020, a reduction of 11.4%. This represents the largest drop in emissions since the ETS began operating in 2005.
Which country in EU is richest
Monaco is not only the richest country in Europe but is also the richest country in the world in terms of GDP per capita.
Which countries benefit most from EU Recovery Fund
On aggregate, seven member states receive about 70% of these EU funds led by Italy, Spain and Poland between 13-15%, followed by France (10%), Romania (6.5%), Germany (6.3%) and Greece (5%).
What are the weaknesses of EU ETS
EU emissions trading: 5 reasons to scrap the ETSThe ETS has not substantially reduced emissions.The EU ETS is used to undermine other climate and emissions control policies.The ETS sets a ceiling on climate ambition.The EU ETS has not been cost-effective and has subsidised polluters at tax payers' expense.
Who are the biggest beneficiaries of EU funds
Poland was the biggest net recipient of the EU budget (getting more back than it contributed in the first place), followed by Greece, Romania, Hungary and Portugal.
Which countries get most money from EU
Poland was the biggest monetary benefactor from the EU, coming out with 11.9 billion euros earned, far ahead of Greece (4.3 billion euros) and Hungary (4.1 billion euros). But being on top of this list doesn't have to send a country scrambling to leave the political union.
Who gets the most money from EU
Poland
In terms of net recipients, Poland leads with EUR 12.9 billion. It is followed by Greece with EUR 4.7 billion and Hungary with EUR 4.3 billion. Romania (EUR 4.2 billion) and Spain (EUR 3.5 billion) take the other places. Looking at the net positions relative to gross national income (GNI), the picture shifts somewhat.
Who is the largest donor of foreign aid
The US is the largest donor country, with ODA at US$47.8 billion in 2021. Relative to economic size, the US ' ODA is low, at 0.2% of GNI , placing the US in 22nd among OECD DAC members.
Who pays for carbon credits
Individuals and companies buy them to compensate for their unavoidable emissions. They're from projects or activities that reduce or remove carbon emissions from the air.
Who buys carbon credits
Absolutely! Farmers and landowners can sell carbon credits because ALL land can store carbon. Landowners are eligible to receive carbon credits at the rate of one per every ton of CO2 their land sequesters. LandGate helps landowners understand how much carbon their land can sequester every year.
What is the most poor country in EU
Among the poorest countries in Europe, Ukraine ranks as the poorest with a GNI per capita of $3,540. Moldova follows closely behind in the second position with a GNI per capita of $4,570. Albania is the third poorest European country, with a GNI per capita of $5,210.
Is EU richer than US
As of 2021, The per capita income of the United States is 1.86 and 1.44 times higher than that of the European Union in nominal and PPP terms, respectively. The US had greater gdp per capita than the EU for data available since 1966.
Which country gets the most money from the EU
Poland
Poland was the biggest monetary benefactor from the EU, coming out with 11.9 billion euros earned, far ahead of Greece (4.3 billion euros) and Hungary (4.1 billion euros). But being on top of this list doesn't have to send a country scrambling to leave the political union.
Who benefits from the EU
Since 1957, the European Union has achieved great things for its citizens and the world:a continent at peace.freedom for its citizens to live, study or work anywhere in the EU.the world's biggest single market.aid and development assistance for millions of people worldwide.
Is UK leaving EU a good thing
Leaving the EU has meant that the UK has not had to contribute to the significant new liabilities arising from the EU's Covid response including, for the first time, the EU's borrowing of up to €750 billion between 2021–24.