Does GDPR cover metadata?
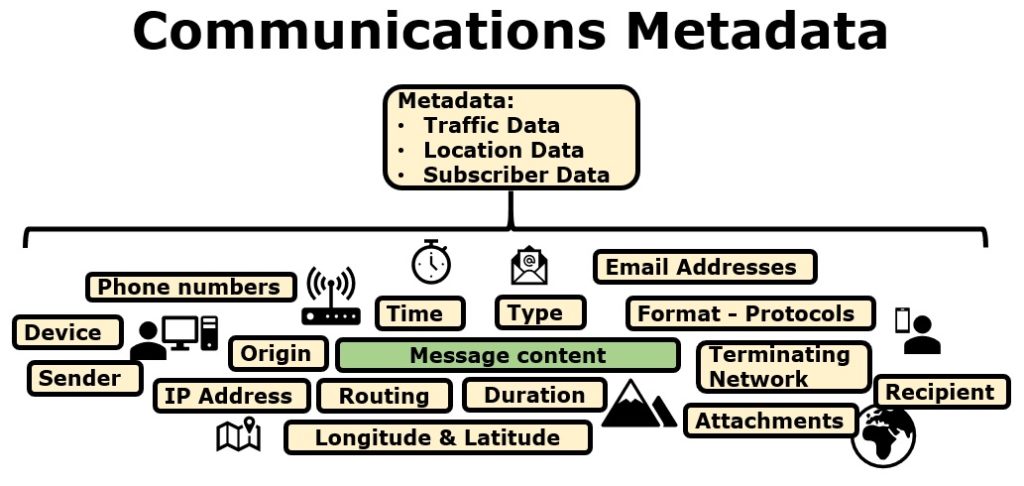
Does GDPR apply to metadata
This means that, for Metadata users, a majority of the information that you collect about your subscribers and contacts is considered personal data under GDPR. Even personal data that has been “pseudonymized” can be considered personal data if the pseudonym can be linked to any individual.
What is metadata in GDPR
It's structured data that helps sort information by different attributes. Metadata summarises basic information about data which can make it easier to find and use. By having the ability to search for data by a specific element, the process of locating documents becomes more straightforward.
What data is not covered by GDPR
Information which is truly anonymous is not covered by the UK GDPR. If information that seems to relate to a particular individual is inaccurate (ie it is factually incorrect or is about a different individual), the information is still personal data, as it relates to that individual.
What type of data does the GDPR cover
The GDPR protects personal data regardless of the technology used for processing that data – it's technology neutral and applies to both automated and manual processing, provided the data is organised in accordance with pre-defined criteria (for example alphabetical order).
Is metadata considered data
Often referred to as data that describes other data, metadata is structured reference data that helps to sort and identify attributes of the information it describes.
Is metadata confidential
While metadata is usually harmless, depending on the context it can sometimes contain privileged, confidential, or sensitive information.
Is metadata a type of data
As the name suggests, metadata is data that describes other data. In other words, it's information that tells you about the data found in your database. For example, we could label a column that looks like just a bunch of numbers with the label “latitude,” which would give that column additional meaning and context.
Does GDPR apply to all data
The EEA GDPR and the UK GDPR apply to all "personal data,” which includes any information relating to a living, identified or identifiable person. Examples include name, SSN, other identification numbers, location data, IP addresses, online cookies, images, email addresses, and content generated by the data subject.
What data is sensitive to GDPR
Definition under the GDPR: data consisting of racial or ethnic origin, political opinions, religious or philosophical beliefs, or trade union membership, genetic data, biometric data, data concerning health or data concerning a natural person's sex life or sexual orientation.
What records are subject to GDPR
What are the records of processing activities (ROPA) Article 30 of the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organisations to maintain internal records, which contain the information of all personal data processing activities carried out by the organisation.
Is metadata part of the document
Regarding documents, Metadata is everything you don't see in the document. It's the structure around what the document is and what it's about. There are many different types of metadata. The most common forms of metadata include structural metadata, administrative metadata, and descriptive metadata.
Is metadata primary data
Though not all data are accompanied by metadata, it is easy to see and understand why metadata are important and valuable when searching for secondary data, as well as when constructing primary data that may be shared in the future. Just as simple files come in all shapes, sizes, and formats, so too do metadata.
Is metadata considered personal data
Any data related to an identified or identifiable natural person is considered personal data and is as such protected under the GDPR. This includes metadata.
Is metadata described as data information
Metadata can be defined as the information that describes and explains data. It provides context with details such as the source, type, owner, and relationships to other data sets, thus helping you understand the relevance of a particular data set and guiding you on how to use it.
Does GDPR only protect digital data
The GDPR covers the processing of this data in several ways, including wholly or partly automated processing, or personal data being processed in a wholly non-automated manner, such as in the case of paper recording being used as part of a 'filing system'.
What does GDPR prohibit
Processing personal data is generally prohibited, unless it is expressly allowed by law, or the data subject has consented to the processing.
What does GDPR not allow
In short, the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) doesn't apply if your business doesn't operate within the EU, doesn't process personal data, or if you're only processing data for domestic purposes.
What are GDPR limitations
You can only use the personal data for a new purpose if either this is compatible with your original purpose, you get consent, or you have a clear obligation or function set out in law.
Does GDPR apply to data subjects
The main purpose of GDPR is to protect the personal data of data subjects—those from whom personal data was collected by a business or an organization.
Is metadata a form of data
Metadata is defined as the data providing information about one or more aspects of the data; it is used to summarize basic information about data that can make tracking and working with specific data easier. Some examples include: Means of creation of the data.
Does GDPR apply to offline data
One of the most common misconceptions is to think that the GDPR only applies to the online environment: it doesn't! The GDPR is technology-neutral: it applies to the processing of personal data no matter how it takes place (online, offline, via a website, via an app, in an employment relationship etc.).
Does GDPR cover all data
The EEA GDPR and the UK GDPR apply to all "personal data,” which includes any information relating to a living, identified or identifiable person. Examples include name, SSN, other identification numbers, location data, IP addresses, online cookies, images, email addresses, and content generated by the data subject.
What are the 7 GDPR requirements
The principles are: Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency; Purpose Limitation; Data Minimisation; Accuracy; Storage Limitations; Integrity and Confidentiality; and Accountability.
What are the four strict requirements that define valid in GDPR
Consent needs to be freely given. Consent needs to be specific, per purpose. Consent needs to be informed. Consent needs to be an unambiguous indication.
What are the 7 data subject rights under GDPR
The GDPR has a chapter on the rights of data subjects (individuals) which includes the right of access, the right to rectification, the right to erasure, the right to restrict processing, the right to data portability, the right to object and the right not to be subject to a decision based solely on automated …